Lecture 7 : 3rd order nonlinearities (part 2)
Résumé de section
-
In a first part, we will describe the so-called Four-Wave Mixing (FWM) interactions occurring in lossless materials. Similarly to parametric interactions in
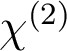 materials, third order optical parametric
amplification process can be exploited to amplify a signal beam by
means of its interaction with a pump beam.
materials, third order optical parametric
amplification process can be exploited to amplify a signal beam by
means of its interaction with a pump beam.Finally, we end the lecture by illustrating resonant nonlinear interactions involving a two-photon transition on the material. It focuses on Raman and Brillouin scattering effects involving the interaction of light respectevely with optical and acoustic phonons in materials.
We first introduce a classical description of spontaneous Raman scattering which originates from the polarizibility fluctuations of molecules due to vibrating modes and provide a quantum description insight of Raman scattering. We will show that Raman scattering can be stimulated by through a double excitation at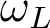 and
and 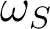 , providing that
, providing that 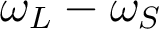 match with the Raman shift
match with the Raman shift 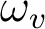 of the molecular material. Under a stimulated regime, the Stokes beam at
of the molecular material. Under a stimulated regime, the Stokes beam at 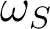 is amplified at the expense of the pump beam at at
is amplified at the expense of the pump beam at at 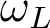 , leading to a cascading regime with the generation of successive Stokes peaks at
, leading to a cascading regime with the generation of successive Stokes peaks at 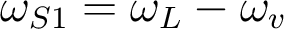 ,
, 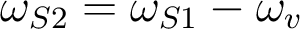 , ..., . Such a Raman cascading effect is used in Raman fiber lasers.LEARNING OUTCOMES OF THE LECTURE
, ..., . Such a Raman cascading effect is used in Raman fiber lasers.LEARNING OUTCOMES OF THE LECTUREBy the end of this lecture, students will know...
- the nonlinear effects that arise in a 3rd order nonlinear materials
By the end of this course, students will be skilled at ...
- Solving the nonlinear equation in parametric situations and derive analytical solutions under the undepleted pump approximation
- Calculating nonlinear interaction performances/efficiencies in situations governed by analytical solutions or expressions
By the end of this course, students will understand ...
Nonlinear effects are a key points in the development of many applications in photonics (especially in relation with laser physics)
- Nonlinear interactions lead to energy transfer between optical beams, and/or between matter and beams, enabling in some cases the realization of nonlinear optical amplification and/or oscillation.
- Nonlinear optics is an essential tool to create novel optical frequencies generated through the interaction of incident beams within nonlinear materials
- Nonlinear effects are subject to phase matching conditions
By the end of this course, students will be able to ...
- Model 3rd order nonlinear effects,
- Evaluate nonlinear interaction performances/efficiencies under approximations that should be specified, explained and justified
- Determine in a situation involving the propagation of at least one light beam through a dielectric material medium (solid or guided), whether non-linear effects can be neglected.
